Bunions, or hallux valgus, are a common foot condition that can cause pain, discomfort, and difficulty in daily activities. This article will provide an in-depth understanding of bunions, including their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. So, let’s dive into the world of bunions and learn more about this prevalent issue.
What is Bunion (Hallux Valgus)?
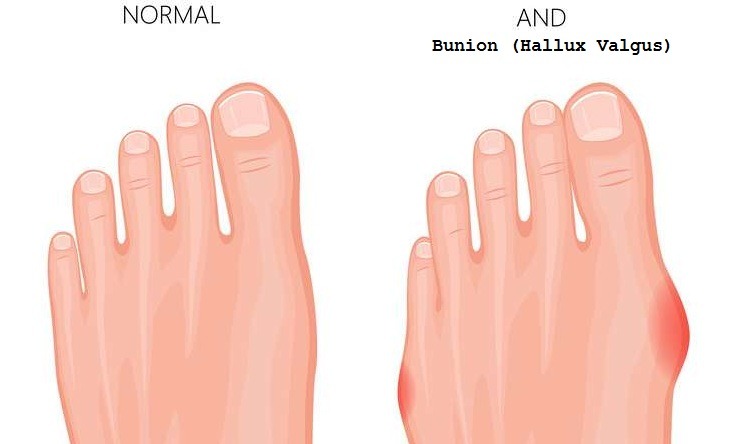
A bunion is a bony bump that forms at the base of the big toe, where it connects to the foot. This bump is the result of the big toe shifting towards the other toes, causing the joint to protrude outward. Over time, this misalignment can cause the joint to become enlarged and painful.
Causes of Bunions
The exact cause of bunions is still debated among experts, but there are several factors that have been associated with their development:
- Genetics: A family history of bunions may increase your risk of developing one, as it is thought that some people may inherit a foot structure that is more prone to bunions.
- Footwear: Wearing tight, narrow, or high-heeled shoes can place pressure on the big toe joint, contributing to the formation of a bunion.
- Foot Structure and Pronation: Flat feet, low arches, or excessive pronation (rolling inwards of the foot) can all contribute to the development of bunions, as these foot structures can lead to instability in the big toe joint.
Symptoms of Bunions
Bunions can present with a range of symptoms, including:
- Visible Deformity: The most obvious sign of a bunion is the protrusion at the base of the big toe.
- Pain and Discomfort: Bunions can cause pain, especially when wearing tight or ill-fitting shoes. The pain may be mild to severe, depending on the size of the bunion and the pressure placed on it.
- Inflammation and Redness: The skin around the bunion may become red, swollen, and tender to touch.
- Limited Mobility: As the bunion progresses, it may become increasingly difficult to move the affected joint, resulting in a decreased range of motion.
Diagnosis of Bunions
A healthcare professional can usually diagnose a bunion through a physical examination of the foot. In some cases, an X-ray may be required to assess the severity of the deformity and to rule out other potential causes of the symptoms.
Treatment Options for Bunions
There are several treatment options available for bunions, which can be broadly categorized into conservative treatments and surgical options:
Conservative Treatments for Bunion
These include wearing proper footwear, using over-the-counter bunionpads or cushions, applying ice packs to reduce inflammation, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers. Custom orthotics or shoe inserts may also be recommended to help redistribute pressure on the foot and alleviate pain.
Surgical Options for Bunion
In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct the deformity and relieve pain. There are various surgical techniques available, and the specific procedure chosen will depend on the individual’s needs and the severity of the bunion. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of surgery with a healthcare professional before making a decision.
Prevention of Bunions
- While it may not be possible to completely prevent bunions, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing them or to slow their progression:
- Choose footwear with a wide toe box and avoid narrow, tight, or high-heeled shoes.
- Maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight can place additional pressure on the feet.
- Use custom orthotics or shoe inserts to provide arch support and reduce the risk of excessive pronation.
- Perform regular foot exercises to help maintain flexibility and strength in the foot muscles and joints.
Frequently Asked Questions About Bunion / Hallux Valgus
- Can bunions be reversed without surgery? In some cases, conservative treatments like wearing proper footwear, using orthotics, and performing foot exercises may help alleviate pain and slow the progression of bunions. However, these measures cannot reverse the bony deformity itself. Surgery is the only option to correct the deformity.
- Do bunions always cause pain? Not all bunions are painful. Some individuals may have a visible bunion but experience no discomfort, while others may have significant pain. The level of pain is often related to the severity of the deformity and the type of footwear worn.
- Are bunions more common in women? Yes, bunions are more prevalent in women, likely due to the wearing of tight, narrow, or high-heeled shoes that can contribute to the development of bunions.
- Can children develop bunions? Although less common, children can develop bunions, often due to genetic factors or underlying foot conditions. It is essential to address these issues early to prevent complications later in life.
- How long does it take to recover from bunion surgery? Recovery time after bunion surgery can vary depending on the specific procedure performed and the individual’s overall health. Generally, it can take anywhere from six weeks to several months for a full recovery. Following your healthcare professional’s advice and adhering to post-operative care instructions can help ensure a smooth recovery.
Complications and Risks Associated with Bunions
Bunions, if left untreated or poorly managed, can lead to several complications and risks:
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the fluid-filled sac (bursa) that cushions the joint can develop, causing pain and swelling around the affected area.
- Hammertoe: Bunions can cause a secondary deformity in the neighboring toes, such as hammertoe, where the toe is bent abnormally at the middle joint. This can lead to additional pain and discomfort.
- Metatarsalgia: The misalignment of the big toe joint can lead to increased pressure on the ball of the foot, causing inflammation and pain in the area, a condition known as metatarsalgia.
- Osteoarthritis: Chronic joint misalignment and the resulting inflammation can contribute to the development of osteoarthritis in the big toe joint, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Conclusion
Bunions are a common foot condition that can cause pain, discomfort, and limited mobility. Understanding the causes and symptoms of bunions is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. While conservative treatments may help alleviate symptoms in mild cases, surgical intervention may be necessary for more severe bunions. Preventative measures, such as wearing appropriate footwear and maintaining good foot health, can help reduce the risk of developing bunions or slow their progression.