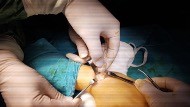
Diagnosis and treatment of many diseases can be achieved with wrist arthroscopy. Wrist arthroscopic interventions replace open surgery in the diagnosis of unspecified pain in the wrist or in the treatment of many known pathological conditions. Thanks to the surgeries performed with the help of a camera through small incisions, the healthy tissues are not damaged and the rehabilitation period is shortened and returning to normal healthy life is accelerated.
Wrist arthroscopy offers numerous benefits in the cleaning of ganglion cysts and wrist inflammation, grading and treatment of wrist calcification (osteoarthritis), treatment of wrist meniscus structure called TFCC, repair of wrist ligament injuries, treatment of fractures of the wrist bones and related calcification (osteoarthritis) mostly in SL ligament.
Cameras and instruments used in wrist arthroscopy are smaller than those used in large joints such as knees and shoulders. The patient is placed on the operating table, preferably with block anesthesia performed by numbing the arm under the armpit, by hanging their hand on a special sling apparatus. Using 2-3 millimeter incisions, mostly from the back of the wrist are used and cameras and instruments enter the wrist joint. Depending on the type of surgery to be performed, the surgical procedure is performed dry or by inflating the joint with serum.
Major Surgeries Performed with Wrist Arthroscopy
Removal of Ganglion Cysts
Ganglion cyst is a cystic swelling caused by herniation of the lining of the joint or tendon sheaths. It is more common in women. While the exact cause of the ganglion cyst is not known, it is associated with anatomical defects or cystic abrasions of the joint capsule and tendon sheaths. There is a ganglion cyst wall consisting of connective tissue and a dense, sticky, colorless, jelly-like liquid. It is mostly observed on the back of the wrist and sometimes on the inside of the wrist. The swelling is the size of a hazelnut.
Recently, the preferred approach in wrist arthroscopy and ganglion removal surgeries is dry procedure that is performed without swelling the joint with water. The cyst is viewed by entering with a camera through a 2 mm incision and the wall and contents of the cyst are cleaned with instruments inserted through a second small incision without damaging the surrounding important tissues. Recovery time with wrist arthroscopy is 3 days, and complete well-being is achieved in 10 days on average.
Another crucial advantage of the surgery of removing the ganglion cyst with wrist arthroscopy is that ligament and meniscus injuries that may occur under the cyst or in other parts of the wrist can be viewed with a camera, and if necessary, treatment can be performed during the same surgery session. Since only the cyst area can be viewed with open surgery, it is not very possible to intervene with other pathologies.
TFCC Injury
TFCC tears may be caused acutely by falling on the wrist over the open hand. Chronic TFCC tears are wear disorders that develop due to age and other rheumatic diseases.
The main symptoms of TFCC injuries are pain and swelling on the side of the 5th finger, a decrease in handgrip strength, and painful clicking with the movement of the wrist.
The first option in the treatment of TFCC injuries is always non-surgical methods. Casts or wrist guards, anti-inflammatory medication treatment or cortisone injections can be used. Surgical treatment is in the agenda in cases of pain that does not respond to these treatments and persists for at least 3 months.
Wrist Ligament Injuries
The most commonly injured ligament is the SL ligament, which connects the scaphoid and lunate bones. It is typical to feel pain in the middle level of the back of the wrist with the backward straining of the wrist. Examination and if possible, MRI with high tesla power are diagnostic.
If the degree of injury is not too high in the treatment, the first option is to follow up with conservative methods such as cast and wrist guards for 6 weeks and then applying physical therapy. If the conservative treatment is not successful, if the degree of injury is high and the distance between the bones is not that wide open, it is possible to treat this with a closed method, in other words, wrist arthroscopy. Cast-splint is applied again for 6 weeks after surgery in wrist arthroscopy. It takes 3 months to return to daily activities without pain, 6 months to return to sports after the surgery.
Visit our HAND AND WRIST DISEASES page to read our articles about your different wrist complaints.